The Centralized Procedure in the GCC Region describes the possibility to register pharmaceutical products throughout the region. The Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf, abbreviated as “GCC” for “Gulf Cooperation Council”, came to exist on May 25th, 1981. The founding Member States are the United Arab Emirates, the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, the Sultanate of Oman, the State of Qatar, the State of Bahrain, and the State of Kuwait.
Since its foundation, the Council has achieved significant legislation harmonization. Its work resulted in the establishment and operation of the GCC Committee for Pharmaceutical Control, GCC Group Purchasing of drugs and medical supplies, etc. Moreover, the centralized procedure and manufacturing sites accreditation unified the drug registration in the region. This article focuses on the:
Pharmaceutical Products Registration: the Centralized Procedure
The Overview of the Procedure and Timelines
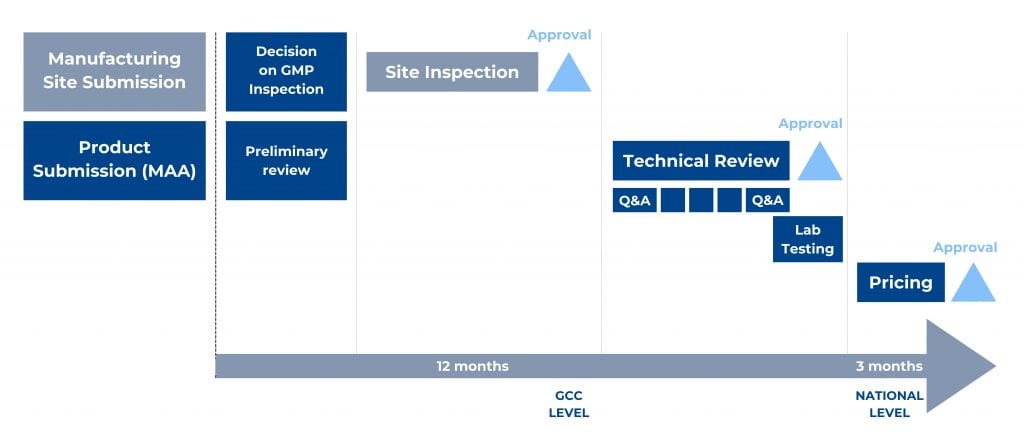 Figure 1. Main steps of the GCC-DR Centralized Procedure and an indicative timeline.
Figure 1. Main steps of the GCC-DR Centralized Procedure and an indicative timeline.
To start the centralized procedure, the Applicant has to submit a registration application for each manufacturing site not accredited by the GCC-DR. In addition, the Applicant should submit the mentioned registration application together with one product marketing authorization application for each desired production line.
A product dossier, prepared as per the GCC CTD format guideline, is first submitted with product samples to the executive office of GCC-DR, reviewed for submission completeness, and dispatched to the member states technical review. Reviews occur separately, then comments from member states are discussed during the upcoming committee meeting. Authorities will notify the Applicant if additional information is required. In such a case, the Committee will review the submitted responses again and again until the provided answers are complete and satisfactory.
Submission in e-CTD format is mandatory since February 2019 and should be done only via the GHC Electronic Gateway. Several documents have been published by GHC, including a guide on “How to Register for the GHC Web Client”, the “GHC Electronic Submission Portal- Naming Convention Files”, and the “Web Client User Guide” to assist applicants.
The region-specific Module 1 has to be prepared according to the “GCC Module 1 Specification and the Baseline eCTD Submission Requirements” guideline of December 2018.
Applicant submits samples, methods, and material for their analysis – which will be done at a laboratory accredited by the Central Committee after issuing a positive opinion on the product application (MAA).
Once the Committee decision is available, the executive office notifies the Applicant and issues the registration certificates for the product and the company/site in case of a favourable opinion. The applicant can appeal the decision within two months from the notification date.
Requirements for the Centralized Procedure in the GCC
The Labelling Requirements
GCC-DR requires that products to be centrally registered/re-registered have:
- The trade name and storage conditions added in Arabic on the outer packaging, unless they are only for hospital use.
- A GS1 Data Matrix barcode on their outer label with the following information:
- GTIN
- Serial Number
- Expiry Date
- Batch/Lot number
The Applicant shall also refer to the GCC Guidance for Presenting the SPC, PIL and Labelling Information and to the GCC Drug Barcoding Specifications.
The Registration Dossier Requirements
The Applicant should prepare MAA in the eCTD format and consider the regional requirements by consulting the pertinent GCC guidelines. The document “GCC Data Requirements for Human Drugs Submission – Content of the Dossier” gives insights into the expected format and content of the application. Module 1 and parts of Module 3 are additionally to be submitted as hard copies.
Applicants for Blood, Vaccines, Sera and Biosimilar products are requested to be included in their application’s additional information according to annex VI of the “Central Registration of Pharmaceutical Companies and their Products” regulation of January 2012 and following other specific guidelines as applicable to each product category.
The Fast-Track Registration and Reliance pathway
In July 2020, GHC published a circular indicating that a reliance model can be applied for products approved in at least 2 GCC countries. In this case, GHC centrally approves the product within 60 calendar days from submitting the scientific reports issued by the GCC countries.
Product Pricing Guidelines
After Central Committee approved both the site and the drug product, the registration procedure must be finalized nationally, including the pricing procedure and registration certificate issuing.
GCC-DR only sets the CIF price – according to the “Pricing Rules of Centrally Registered Medicinal Products” of November 2011 and the price certificate Form submitted by the Applicant. In practice, the Applicant submits the GCC approved CIF price to each member state and receives a national product registration certificate with the approved wholesale and retail prices.
The Centralized Procedure offers an alternative pathway to accessing the Gulf pharma markets. While the procedure seemed lengthy and lacking predictability and transparency in the beginning, it has recently experienced improvements:
- More frequent Committee meetings
- Establishment of an Online Portal for managing submission and communication
- The publishing of numerous guidance documents and detailed guidelines.
The most cited advantages of the central registration in comparison to national procedures are:
- The recognition by 7 countries of site and product approvals
- The harmonized requirements resulting in ‘one’ product dossier
- The open way to the participation in the Secretariat of Gulf Health tenders.
Nevertheless, other important factors, including product-related aspects, are imperative to consider when planning the Regulatory Strategy for the GCC countries.
Finalization of the European Database on Medical Devices (Eudamed) Regulation Implementation
There is an increased demand for Materiovigilance solutions in recent years as the usage of medical devices keeps growing. Current industry changes are already impacting future developments, and it is becoming more and more challenging to keep up with recent...
Download – ABO Whitepaper
Whitepaper Regulatory Affairs Outsourcing Affiliate-Based Outsourcing for Regulatory Affairs acts as an addition or replacement of your in-house local regulatory capabilities. However, it frequently falls short of meeting the requirements for effective organization,...
What is the Clinical Trials Regulation?
The EU CTR is the new Regulation that govers all interventional clinical trials using human medicinal products. By implementing this Clinical Trials Regulation (CTR) early 2022, the European Commission hopes to establish a better environment for clinical trials in the...









